USC IP PARTNERSHIP V META , FEDERAL CIRCUIT 2023 (SOFTWARE PATENTS)
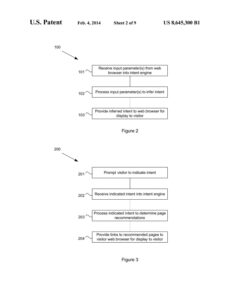 USC brought suit for infringement against Facebook, Inc. (now Meta Platforms, Inc.), asserting that its “News Feed” feature infringes claims 1–17 of U.S. Patent No. 8,645,300. The software patent relates to a search engine software method for predicting which webpages to recommend to a web visitor based on inferences of the visitor’s “intent.” The software patent states that website navigation can be enhanced “by recording a visitor’s intent and recording page rankings that indicate how well the pages of a website match the visitor’s intent.” The software patent further explains that visitor intent can be inferred from historical intent data, the Uniform Resource Locator, the user’s visits, and optional user intent confirmation. The lower court, the Western District…
USC brought suit for infringement against Facebook, Inc. (now Meta Platforms, Inc.), asserting that its “News Feed” feature infringes claims 1–17 of U.S. Patent No. 8,645,300. The software patent relates to a search engine software method for predicting which webpages to recommend to a web visitor based on inferences of the visitor’s “intent.” The software patent states that website navigation can be enhanced “by recording a visitor’s intent and recording page rankings that indicate how well the pages of a website match the visitor’s intent.” The software patent further explains that visitor intent can be inferred from historical intent data, the Uniform Resource Locator, the user’s visits, and optional user intent confirmation. The lower court, the Western District…
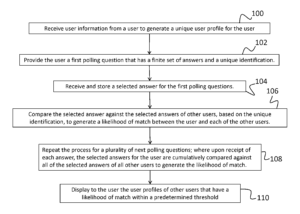 Trinity Info Media, LLC sued Covalent, Inc. for infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 9,087,321 and 10,936,685 relating to methods and systems for connecting users based on their answers to polling questions. U.S. Patent No. 9,087,321 teaches that its claimed invention is “directed to a poll-based networking system that connects users based on similarities as determined through poll answering and provides real-time results to the users. The claimed invention of the ’685 patent is “directed to a poll-based networking and ecommerce system that connects users to other users, or products, goods and/or services based on similarities as determined through poll answering and provides real-time results to the users.
Trinity Info Media, LLC sued Covalent, Inc. for infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 9,087,321 and 10,936,685 relating to methods and systems for connecting users based on their answers to polling questions. U.S. Patent No. 9,087,321 teaches that its claimed invention is “directed to a poll-based networking system that connects users based on similarities as determined through poll answering and provides real-time results to the users. The claimed invention of the ’685 patent is “directed to a poll-based networking and ecommerce system that connects users to other users, or products, goods and/or services based on similarities as determined through poll answering and provides real-time results to the users. A multi-format digital video product system capable of maintaining full-bandwidth resolution while providing professional quality editing and manipulation of images, which is capable of conserving bandwidth while preserving data is not patent-eligible.
A multi-format digital video product system capable of maintaining full-bandwidth resolution while providing professional quality editing and manipulation of images, which is capable of conserving bandwidth while preserving data is not patent-eligible. The ITC took 35 U.S.C.
The ITC took 35 U.S.C.  Though creating digital location histories is not patent eligible, a method of enhancing digital search results may be patent eligible.
Though creating digital location histories is not patent eligible, a method of enhancing digital search results may be patent eligible. Functionally recited claims to organizing and displaying visual information are not patent-eligible.
Functionally recited claims to organizing and displaying visual information are not patent-eligible. At the pleadings stage, all that is required to survive a motion to dismiss based on Alice are plausible allegations in a complaint that the claims are patent-eligible.
At the pleadings stage, all that is required to survive a motion to dismiss based on Alice are plausible allegations in a complaint that the claims are patent-eligible. Mr. Smith’s argued that the first step in analyzing a claim must be to determine whether the claim is useful. And if it is useful, it is by law patent-eligible. The Federal Circuit disagreed.
Mr. Smith’s argued that the first step in analyzing a claim must be to determine whether the claim is useful. And if it is useful, it is by law patent-eligible. The Federal Circuit disagreed. A system and method for determining eligibility for Social Security Disability Insurance benefits by computer is directed to steps that can be performed in the human mind, or by a human using a pen and paper and is therefore a patent-ineligible abstract idea.
A system and method for determining eligibility for Social Security Disability Insurance benefits by computer is directed to steps that can be performed in the human mind, or by a human using a pen and paper and is therefore a patent-ineligible abstract idea.